Most Important Productivity Management Metrics
Most Important Productivity Management Metrics
An organization aims to churn as much productivity as possible. Productivity management metrics are measurements that help define the situation of your office, and it helps to visualize how fast and productively your team is giving outputs.
Looking at productivity metrics helps derive conclusions about where the institution is heading.
The productivity metric at present is an asset for the future as the past matric result helps the work presented, and the present matric will be a reflection of the future productivity index.
Why Productivity Metric and What Makes It Different?
Productivity refers to efficiency, whereas metric refers to measurement. In management, the productivity of one’s employees is measured by the employer.
It has an inclusion of change management and a matrix for time management. In a simple sense, productivity refers to:
Productivity = Output/ Input
When choosing productivity management metrics, one should know what type is used. The decision matrix helps in spending time on what matters. There are different types of matrices that are either based on volume, conversion, revenue.
Productivity Management Metrics are unique as they improve and take care of performance and point out which spot improvement is required. The productivity metric is different from other matrices like the quality metric.
These metrics act as the warning signs that alert whether any system will work or it’s about to crash shortly.
One needs patience, a level of understanding, and an analytical mindset to understand productivity metrics exactly.
Productivity Management Metrics: Actual Meaning
Productivity management metrics state whether the goals of productivity are met or not. These are the points that clarify the level of work productivity generated from the work employees do.
It can track and measure how fast and effective workers are doing their assigned work. Tracking also includes conducting overall work with necessary time tracking software and tools.
Productivity management metrics provide answerability to the following questions:
- What kind of projects delivered more outputs and profits as per the effort and resources?
- Which projects demanded more expenses but fewer outputs
- Which teams require more tools and beneficiaries to conduct work effectively?
- How to detect the point of focus for maximum profit of an organization?
ProductProductivity management metrics are needed for giving feedback to the employees. The managers can use Productivity management metrics to derive conclusions and collect facts and details with an opinion.
How does Productivity Metrics work?
The productivity metric works in rating and estimating employees who produce products and products that give services to customers.
For quality indication, employees, products, and services are kept in mind for the organization’s development.
Productivity metric works as follows:
- Setting an index for comparison and evaluation of the process.
- Analyze and weigh the result.
- Compare the index with the result.
One of the important metrics is task management which is possible using the Eisenhower box and the Eisenhower matrix.
This matrix helps figure out which task to do first and emphasizes urgent and important tasks.
Efficiency of Process and Productivity Metric
The quality metrics always produce results in the form of a percentage, and the productivity metric shows the ratio that is directly between two units of measurement.
- One that measures resources applied.
- Other quantifying the output.
It is important to identify documents and reports with resources and outputs to measure productivity.
If the necessities are not identified properly, the results generated do not correlate with real-life situations. This situation affects the overall plan for the performance and development of the company.
The company processes are essential for productivity metrics as there is always a relation of one process’s output that can be the resource for another process.
The efficiency of processes is very important for productivity metrics. It is equally important for time managers to use a time management matrix with tips to manage employees’ time to move towards their goals.
KPIs and Productivity Management Metrics with Benefits
Key Performances Indicators indicate the level of progress for the wanted result. Within the KPIs, one can derive what your business is like and how well employees perform.
At one point, KPIs and Productivity Metrics interlace.
The goals of sales and profit margin fall under the performance metric examples. But in reality, they go deeper as sales bring profits.
The profits themselves require management, which is influenced by the metric used to scale productivity for the whole business. The prioritization framework helps in the completion of urgent tasks.
The performance metrics are important, and these metrics help not only one part or department but aid the overall branches for better productivity.
The departments include customer service, human resources, management, and others, benefiting from productivity metrics.
Why Calculate Productivity?
A team is productive if it meets the following criteria:
- Meet deadlines and work to complete as many tasks.
- High-quality output delivery.
- Efficient work in fixed or little time duration.
The profit is directly proportional to the quality of work accomplished by employees. When you calculate productivity, you can estimate, find and solve problems before projects go out of hand financially.
The calculation is easier with the use of reliable budget managing applications.
It is easier to set, reset, change and achieve the desired goal from the performance metric.
In remote working, the individual metrics act powerfully, and managers can have a far-sight as to how the employees are working.
When changes or patterns are detected, managers can check up on the employees.
Requirements To Calculate Productivity Metrics
Observations are essential, but more than that, data and facts are essential to calculate productivity.
It is not necessary that employees, if present, are working their best or just being present in the office does not conclude that they are working the best they can without getting distracted.
Such assumptions are invalid until you check employee performance individually. The lack of communication, especially during remote work, can hamper productivity and lead to losses in the company.
So, correct data can clarify calculations for the derivation of productivity measures.
1. Choose Correct Metric
The workers in your company can’t work for every second in the company. So it would help if you had proper metrics and data for calculating productivity.
The importance of data is further clear with an example of the productivity of sending emails.
To calculate how productively the emails are sent and what data are needed to derive productivity of one single task is as follows:
- How many other companies were the emails delivered yesterday?
- How were many emails from other companies received?
- It is to provide a score to email following its importance. The rating criteria are from 1 to 10.
- How did the incoming and outgoing emails affect your daily work routine?
From the above email example, you can derive how fruitful sending email is and how adversely it affects daily productivity.
2. Determining Productivity Metric Further
The productivity metric is usually used in business for sales and revenue. You can derive productivity metrics for almost anything, and it is to derive outputs from deciding the following:
- How is a measurement of the results possible?
- What activities lead to demanded outcomes?
- What is the desired outcome?
- Do the measured activities lead to demanded output?
For instance, you have to measure how productive a single employee is when calling for sales. Here are a few requirements you need to fulfill for evaluation:
- Select Period: Figure out the basis of measurement, whether daily, weekly, hourly or monthly.
- Measurement of Outcome: For each employee, note down the number of phone calls they make according to the input time.
- Find the Input Figure: The input figure is the time dedicated by the employees to make a call or the total number of calls.
- Division of Output: Divide the output by input with a number like 200 calls per week.
- Assignment of Values: This value will help measure the costs and benefits of the employees who invested time and made calls.
The above points can help determine how productive the employees are at making calls. The Eisenhower method can help them take immediate action and conduct urgent and important activities.
This same formula is adaptable for other calculations, too, when you spend your time calculating productivity metrics.
Calculation of Productivity Metrics
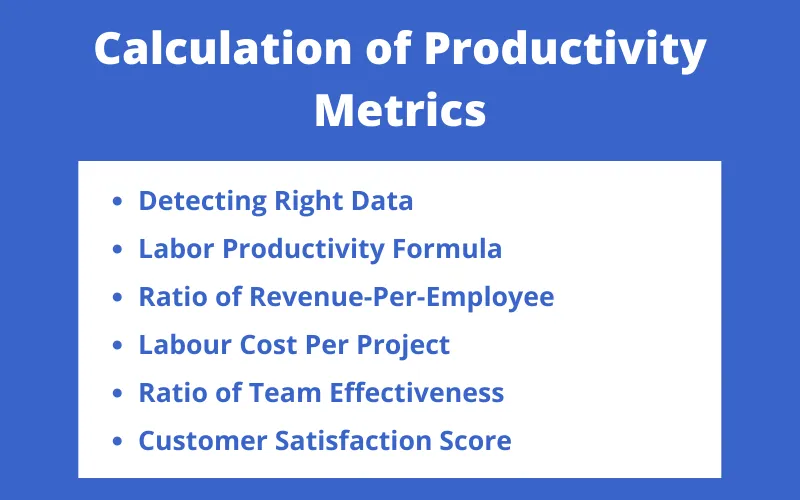
The calculation of productivity involves several steps. Business owners need their hacks to improve productivity.
The ways and methods for calculation of productivity management metrics are given below:
1. Detecting Right Data
It would help if you had a good collection of data for productivity management metrics to meet your company’s goals.
The correct data act as raw materials, and they are gettable and observable in the following ways:
Working Hours
It is important to know how your employees spend their time and how qualitatively it is spent on the work assigned.
The priority matrix can help in deciding which task to do first. Companies have adopted some ways or other for tracking and figuring out the total working hours of employees.
It can be via traditional attendance using papers or some time tracking applications installed into individual workers’ systems.
The more accurate the application is, the better is the tracking of productivity for tracking time with productivity.
Time Per Task
Every employee is assigned tasks, but it is essential to know which one takes time to complete tasks without procrastination.
Time per task can compare the different tasks concerning time and productivity, and a conclusion is derivable stating what type of work is better done by which employees in what time.
It is also how long it takes to give out perfect outcomes. A time tracker can record the task done by an employee for an assignment, and you can know how many hours one spent on that daily task.
Score of Quality
Your employees may spend hours and hours to complete a task, and it may seem like the results generated are huge.
But the actual judgment of the outcome is via quality of work, and it is equally important to look at the quality of the work with quantity. The decision matrix boosts the deciding ability.
Data include click-through rates, customer satisfaction scores, and defect escapes. You can think about scanning if your team meets the quality goals.
For example, one can judge the quality via the performance, not by liking.
Total Profit
This data is usually present to track revenue weekly or monthly, considering the product category. There can be the generation of reports and
That shows how revenue is generated from each component or part of the work and which parts need immediate attention.
For instance, you can know how much revenue each advertisement generates from the report with percentages.
Completion of Task
The system to track work or tasks is the best to derive information on task completion without wasting time.
For tracking, a project management tool is used, or another method of task record-keeping is possible that may require immediate attention.
Without tracking tasks, the entire organization of team coordination can fall apart. Employees require tips for better productivity, and this step includes how you spend time to improve your time management and complete the task.
2. Labor Productivity Formula
This simple formula needs input and output for comparison. Labour productivity is an indicator of productivity, and companies use this formula to calculate revenue to total work hours.
Labour Productivity Formula = Total revenue in certain time duration (input) / Total work hours in that time duration (output)
It is useful to calculate the average productivity in the entire organization even when you have to calculate specific productivity. An example elaborates the explanation:
There is an online store, and you want to analyze which communication medium is more supportive: the chatting one or the call one. For this test, six people team up to track the task and time.
I.e., you have the data you require.
First, you calculate the total products sold via call last month that summed to 4560, and you divide the total hours your team invested in the calls, i.e., 60. The output by input gives 76 sales per hour on the phone.
Your team made 5678 sales through online web chatting by investing 70 hours. The labor productivity formula concludes a total of 81 sales.
So this shows that the chat system is more productive than the telephone one. There are a few drawbacks to the labor productivity formula:
- This formula does not indicate quality.
- It does not classify complexity, and employees’ performance and productivity are unknown as the inputs are considered evenly.
The calculation is basic and does not include the total time spent on other things like:
- Personal development and other works that do not directly contribute to the generation of revenue.
3. Ratio of Revenue-Per-Employee
This ratio is similar to the labor productivity formula, showing how the whole team performs. The mathematical revenue-per-employee formula is written as:
Revenue-per-employee = total revenue/ total number of employees
Revenue-per-employee is suitable for companies that:
- Work as marketing agencies and performance-based businesses.
- Focus on keeping labor costs low to have maximum profit.
4. Labour Cost Per Project
In a company, labor is the major investment. It’s okay when all the team members are equally effective in their work.
But there are cases of over-budget when you pay for time on which employees did not put much effort.
There are time tracking tools for tracking work per hour. There is no need to wait for project completion to begin tracking, as if the budget gets too much, it’s too late to fix the rate.
When there is no presence of a project manager, you can set up points on your own to stay within budget.
This metric is important to know:
- How efficiently your team works.
- For a proper picture of team productivity, you should track quality, quantity, and efficiency.
5. Ratio of Team Effectiveness
The ratio of team effectiveness holds a comparison between profit and time spent on employee salaries. Mathematically,
Team Effectiveness = Gross Profit / Employee Payroll Cost.
The goal of this ratio is :
- To show if investment in your employees is worth it.
- It uses gross profit instead of total revenue.
This ratio is essential in the growth phase when you have decided to add more members. For adding more team members, you have to keep checking the ratio of team effectiveness.
6. Customer Satisfaction Score
Customer satisfaction scores are set to evaluate the level of satisfaction customers gain from the services provided by the company.
The use of surveys gathers the data. After the customer has been shopping or purchasing, they require time to use the product and give proper feedback.
You can email them about the product or ask them in person the next time they visit the store. These feedbacks and recommendations are very useful to derive conclusions.
For ease, online surveys are conducted using tools that send automated emails for feedback. The automatic emails help in the stress management of employees too. The ratings on feedback give an idea of how happy customers are.
The customer satisfaction score gives an idea about the overall quality of output. It is important to note the quality of service to know customers’ true feelings.
Some Examples of Employee Productivity Metrics
Different companies define productivity in different ways keeping in mind the due dates for result generation.
The first and foremost requirement for a productivity metric is an efficient plan for enhancing productivity. For defining productivity in its ways, here are some productivity metrics:
Productivity Metric for E-commerce
Online store holders are very good at advertising and tracking marketing campaigns in social media but sometimes care less about the offices they work from.
Every online business holder needs someone to maintain the website for the proper business flow.
Looking after the site, one should make sure the site is functional and performs well. If there is some problem with your site, it will create a lot of loss.
As the number of sales increases, so will the customer feedback and need for assistance from your company. This situation demands attention from site holders to check up on productivity metrics.
It would help if you decided how much to invest in customer service and watched overtime carefully. Track the investment results and decide if it was a good investment or not.
Productivity Metric for Sales
The best way to measure productivity metrics regarding sales is to calculate the revenue generated per head by the salesperson.
This ratio measures the result and profit per salesperson are related to payroll. Another method for sales is to track the calls sent, focusing on the salesman’s actions.
The result-oriented and action-oriented metrics are essential, but you can also try activity-based metrics. But it is always beneficial to put more emphasis on results.
Productivity Metrics in Agile
The agile framework includes dividing work into modules, i.e., projects with time bondage and clearer methodology. This breakdown structure of agile helps in properly tracking productivity in each step.
The agile productivity tracking includes time cycles, planned-to-done ratios, and defects escaped.
These metrics are great for developer productivity metrics. One cycle refers to the time taken to complete a task, and if the task exceeds the time limit, there is a drain on productivity.
The planned-to-done ratio gives a measure of the outcome concerning what was planned.
When there is a change in the project plan, the team members have difficulty being productive. If projects are planned, they must end, and else, it creates a lot of problems.
Several bugs in a project can also give a metric for productivity, which specifies the quality of work done by team members.
Customer Service Metrics
Customer service is productive when they help and take care of customers on time and take action immediately. The productivity metrics should always be in direct notion with customer service.
When measuring the productivity metric of customer service, make sure you don’t focus too much on the results to put the salesperson in a rush that they end up calling quickly or remain properly engaged on chat. They must enjoy the work and give out better results and productivity.
Productivity Metric Cognizance
After calculating productivity metrics, you still have chances to derive other conclusions.
The measurement is not only for how much work or effort is out for productivity, but the graphs, facts, and figures give real insight and vision into how the work leads to output.
The measurement of productivity helps the overall team members to grow together. Top business executives can use productivity metrics to build strategies.
For instance, if the productivity from manufacturing is not high, there are other things like expanding product lines to avoid that will make the process complex.
Benchmarking Productivity Metrics
You have calculated the productivity metric, but the thing to think about is whether it is good enough or not.
Metrics are numbers that let you know about the situation, but the conclusion is derived from comparing them to your goal or benchmark.
For each productivity metric, it is better to set a benchmark. The benchmarks of companies remain a secret, and the journals that write about different companies also do not reveal such important data.
For setting the proper benchmark, remember the following points:
- The average number for the whole team.
- To jot down the average number for the best performers.
- To make a list of the best number from top performers.
- The number needed for meeting overall business goals.
Benchmarks are better when they are a little higher than average performance, and a huge gap between the present performance and benchmark is not a good sign.
However, you cannot put on a very high benchmark as that goal is hard to reach. Choosing the right benchmark makes it easier to reach its overall goals.
Conclusion
Decide on the metrics you want to track on a weekly, monthly, or yearly basis with the help of time management applications to meet deadlines. Jot down and make a list of the raw data you will require.
Have a look at data from the past so you can figure out the present situation and predict the future.
If there is a lack of data, then make an action plan. What tracking tools and software do you need? Which area is lagging? Decide where the flow of productivity is going and start the calculation.

 in Melbourne
in Melbourne 
 Employee Screen Monitoring Software
Employee Screen Monitoring Software App and Website Monitoring Software
App and Website Monitoring Software Time and Attendance Software
Time and Attendance Software Finance
Finance Banking
Banking Healthcare
Healthcare Lawyers
Lawyers Retail & ecommerce
Retail & ecommerce Knowledge base
Knowledge base Blogs
Blogs Installation Guide
Installation Guide FAQs
FAQs About
About Media Kit
Media Kit Contact us
Contact us